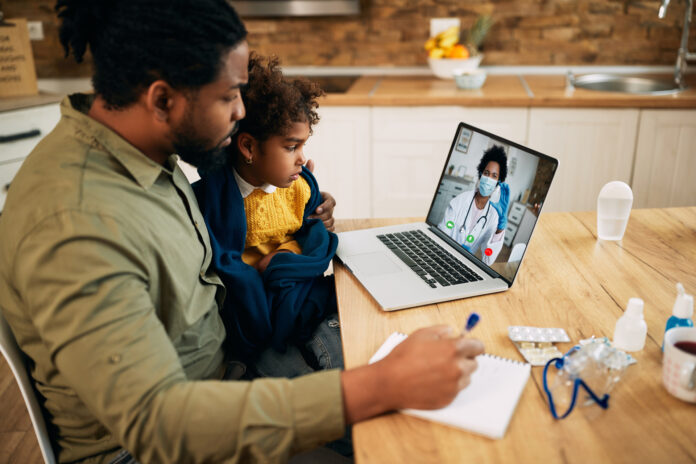
Millions of individuals around the world are afflicted by mental health illnesses, including depression and anxiety. These disorders are frequently referred to as “invisible illnesses” because their main symptoms are emotional and psychological.
Despite their invisible nature, the impact of Telehealth For Depression and anxiety can be profound, affecting not only the people who suffer from them, but also their families, communities and societies as a whole.
In this comprehensive article, we will explore the nature, causes, symptoms, treatments and broader social context of depression and anxiety, shedding light on these common, yet often misunderstood, mental health conditions.
Section I: Depression
1 Understanding depression
Depression, often called major depressive disorder (MDD), is a mood disorder characterized by persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and lack of interest or pleasure in activities. It is a pervasive and chronic condition that can have a substantial impact on a person’s capacity to function in daily life. It is not just a passing emotional reaction to life’s hardships.
2 Prevalence and Impact
Depression is a leading cause of disability worldwide, affecting people of all ages, races and backgrounds. Depression can lead to a variety of negative outcomes, including reduced quality of life, impaired work and academic performance, and increased risk of suicide.
3 Causes and risk factors
Depression is a complex condition with multiple contributing factors, including:
Biological factors: Imbalances in brain chemistry, genetics, and hormonal changes can influence depression.
Psychological factors: Negative thinking patterns, low self-esteem, and unresolved trauma or grief can contribute to the development of depression.
4 Symptoms
Depression is characterized by a variety of emotional, physical, and cognitive symptoms, including:
- Persistent sadness or bad mood.
- Fatigue or loss of energy.
- Changes in appetite or weight.
- Sleep disturbances (insomnia or excessive sleeping)
- Feelings of worthlessness or excessive guilt.
- Difficulty concentrating or making decisions.
- Thoughts of death or suicide.
5 Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosing depression typically involves a comprehensive evaluation by a mental health professional, including a detailed review of symptoms, medical history, and a mental status examination. Treatment options for depression include:
Psychotherapy: Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), interpersonal therapy (IPT), and psychodynamic therapy are among the therapeutic approaches used to treat depression.
Lifestyle changes: Regular physical activity, a balanced diet, adequate sleep, and stress management can help improve mood.
Support Groups: Participating in support groups or seeking support from friends and family can be invaluable in coping with depression.
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT): In severe cases of depression that do not respond to other treatments, ECT may be considered.
6 Social context
Stigma and lack of awareness around mental health issues often prevent people from seeking help. Initiatives to raise awareness, reduce stigma and improve access to mental health services are essential to addressing the social impact of depression.
Section II: Anxiety
1 Understanding anxiety
Anxiety disorders are a group of mental health conditions characterized by excessive worry, fear, or nervousness that can interfere with daily functioning. These disorders encompass several subtypes, including generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), panic disorder, social anxiety disorder, and specific phobias.
2 Prevalence and Impact
Anxiety disorders are among the most common mental health disorders, affecting approximately 275 million people worldwide, according to the WHO.
3 Causes and risk factors
Anxiety disorders are influenced by a combination of genetic, biological, environmental and psychological factors, including:
- Genetics: A family history of anxiety disorders may increase the risk.
- Environmental stressors: Traumatic experiences, chronic stress, or exposure to a hostile environment can contribute to anxiety disorders.
4 Symptoms
The symptoms of anxiety disorders:
- Excessive worry or fear
- Restlessness or irritability
- Muscle tension
- racing thoughts
- Sleep disorders
- Panic attacks (sudden, intense episodes of fear)
- Avoidance of feared situations or objects.
5 Diagnosis and Treatment
The diagnosis of anxiety disorders involves a comprehensive evaluation by a mental health professional. Treatment options for anxiety disorders include:
- Psychotherapy: Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), exposure therapy, and relaxation techniques are commonly used to treat anxiety.
- Lifestyle modifications: Stress management, regular exercise, a healthy diet, and adequate sleep can help manage anxiety.
- Support Groups: Peer support can provide valuable coping strategies and reassurance for people with anxiety disorders.
Conclusion
Depression and anxiety are two of the most prevalent mental health conditions globally, affecting millions of people across various demographic groups. These conditions, characterized by persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, excessive worry, and fear, can have a profound impact on the lives of those who experience them.
Understanding the causes, symptoms, and available treatments for depression and anxiety is critical to promoting Best Depression Treatment Centers, mental health awareness and reducing stigma.
Efforts to improve mental health education, increase access to mental health services, and reduce stigma are essential to addressing the challenges posed by depression and anxiety. By fostering a more compassionate and informed society, we can better support those affected by these mental health conditions and work to improve the well-being of all.